It is challenging to manually manage Corrective and Preventative Action (CAPA) process with paper based or Excel file system. Here are some of the key features to consider when selecting a Corrective and Preventative Action (CAPA) software solution. The automated CAPA Software helps to comply with FDA inspection requirements.
1.0 Reference or Linkage to Source
There are many sources of nonformities, potential non conformities, quality data, including trends that may indicate action to correct potential or existing product or quality issues, and to develop Corrective and Preventative Action (CAPA) to prevent their occurrence/recurrence. You should be able to analyze the trends and link the CAPA to specific quality events or multiple quality issue records.
The following data sources are used as input for Corrective and Preventative Action CAPA system. Based on the risk analysis of trends or potential impact to the Quality System, a CAPA record will be created.
(1) OOS (out of spec) records for process or products
(2) Customer complaints
(3) Internal audit findings
(4) 3rd Party audit findings
(5) Calibration and Maintenance failures
(6) Supplier Quality Issues
(7) Effectiveness failure of previous CAPA
(8) The CAPA records can be created and maintained in the Qualcy eQMS CAPA module, or the records can be manually created and maintained in a Corrective and Preventative Action (CAPA) software. If Qualcy EQMS module is used for CAPA record, the Issue Risk Assessment form can attached under the Background Tab, or you can reference the Risk Assessment project ID from the Risk Management module. Then the automated work flow can be used.
2.0 Option to Define the Roles and Responsibility
You shall be able to define and assign the following roles
CAPA Owner shall:
Ensure that the CAPA investigation is detailed, thorough and appropriate. The CAPA investigation is completed in timely manner. The CAPA action items are implemented in timely manner.
CAPA Reviewer shall:
The CAPA investigation results are thorough and detailed enough. The planned corrective action or preventative actions are justified for the level of risk involved.
3.0 Options to Record the CAPA Requirements
(1) Containment Action or Correction: Short term action(s) to correct the immediate cause or problem identified. Corrections are typically one-time fixes, but they me be done along with a corrective action if the problem reoccurs or otherwise persists.
(2) Root Cause Analysis: An investigation that results in the identification of the actual cause, or cause(s) of the problem that resulted in the non conformance. Root Cause analysis helps to identify What, How, and why something happened. This effort extends beyond the effects of the problem to discover its most fundamental cause.
(3) Corrective Action: Long term action(s) taken to eliminate the cause of nonconformities in order to prevent the reoccurrence.
(4) Preventive action: Action taken to eliminate the causes of the potential non conformities in order to prevent their reoccurrence.
(5) Effectiveness – the extent to which planned activities are realized and planned results achieved.
4.0 CAPA Workflow
Issue Risk Assessment and CAPA Initiation:
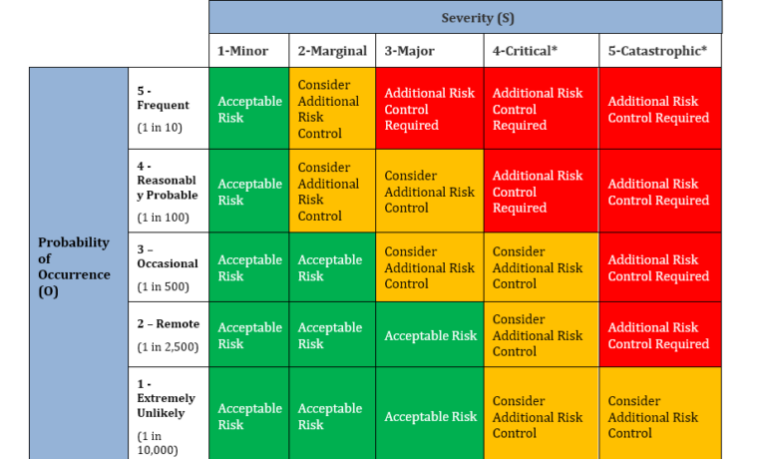
(1) The Quality Department shall be responsible for completing the risk assessment of the data sources using the Issue Risk Assessment which can be done in the Corrective and Preventative Action (CAPA) software. After the assignment of severity and probability numbers for the issue, review the risk assessment matrix. If the combined risk (Severity X Probability) falls within the high risk area, then a new Corrective and Preventative Action project (CAPA) shall be initiated. If the combined risk (Severity X Probability) falls within medium risk area, you may decide to open or not open a new CAPA. If the combined risk falls within the low risk area, then no new CAPA will be opened.
(2) Once the Corrective and Preventative Action (CAPA) is initiated, the system shall assign the CAPA log number and assign the CAPA owner.
(3) The CAPA owner will determine if any containment action or short term correction is required.
(4) If containment action is required the CAPA owner will update the CAPA initiation form inside the CAPA Background page with following information. The details of containment actions are required, the person responsible for completing the containment actions, the due dates for containment actions are expected to be completed. The CAPA owner will make sure that the planned containment actions are implemented as per the schedule.
CAPA Investigation:
(1) Then CAPA owner will start root cause analysis. The analytical tools like, process mapping, Fish bone diagram, cause and effect matrix, 5-Why, IS-IS NOT table and others may be used as appropriate. The summary of the investigation shall include
->Results of review of data sources and records (data, process, operations and/or other sources of information),
->Identification of failure modes (as applicable) and justifications as to how probable root causes were eliminated and why the selected root causes are going to resolve the issues,
->Root cause investigation methodology or tools used to determine and verify root cause(s),
->Conclusions regarding root cause(s).
You can refer to FDA guide on root cause investigation for a CAPA.
(2) Once the root cause analysis is completed, a summary of the root causes found will be updated in the CAPA form built in the Corrective and Preventative Action (CAPA) software.
(3) Then the proposed corrective actions will be developed and updated in the CAPA Software. This should include the details of corrective actions planned, the responsible person for completing the corrective action, the due date for corrective actions are that are expected to be completed.
(4) Then the CAPA form will be submitted to the Approver for review. If the investigation results are rejected by the Approver, the Approver shall provide reason for rejection.
CAPA Implementation
The CAPA owner will verify or validate the corrective action to ensure that such actions are effective and does not adversely affect the finished product or service levels if process/product changes are required.
(1) The proposed Corrective Actions are to be discussed with other employees if they are going to be impacted.
(2) If the proposed Corrective and Preventative Action involve changes to the documents and specifications, then the proposed changes are to be documented, reviewed and approved via the CCR (change control request) record in the Qualcy EQMS system.
(3) The action items may be implemented following the documentation, review and approval of variance records if the CCR is not finalized.
(4) The CAPA owner will verify that the proposed corrective actions do not adversely impact any of the QMS processes or quality of the products.
(5) During the implementation of the corrective actions, if the plan is changed or additional actions are required to be included in the plan, then the CAPA owner will update the CAPA from and submit for review as needed.
(6) The CAPA form may be submitted intermittently for review. The Quality Manager or designee will review the status of the corrective actions in regular intervals depending upon the actions and timelines mentioned in the corrective action plan.
(7) After completion of all the corrective actions, then define and document the Effectiveness Verification Plan in the CAPA form. The Effectiveness verification plan shall include the data collection/analysis or audit activities and the corresponding acceptance criteria that are required to demonstrate success in eliminating or mitigating the issue defined in the Problem Statement.
(8) Once all the corrective actions in the plan are implemented, and Effectiveness verification plans are documented, an updated CAPA form will be submitted to the QA Manager for review of the status of the corrective actions.
(9) The CAPA Approver will review and sign off if the status of the corrective actions is accepted. If the status of the corrective actions is not accepted, then the General Manager/QA Manager will update the CAPA form with any additional requirements and return the CAPA form to the CAPA owner.
(10) Then the CAPA owner will review the CAPA form and may repeat the above sections as required.
(11) Once the QA Manager accepts the status of the corrective actions, the CAPA will be considered as complete.
CAPA Effectiveness Verification
The CAPA owner will update the effectiveness section of the CAPA Form when the effectiveness verification results are available. The updated CAPA Form will be submitted to the QA Manager for review. If the effectiveness verification is accepted, then the Corrective and Preventative Action (CAPA) will be considered as closed. If the effectiveness verification is not accepted, the CAPA is reopened. A new CAPA will be opened and the old CAPA number will be referenced.
(1) CAPA for Preventative Actions:
->When potential non conformities are identified based on the analysis of data as per section 2.1, and then the risk assessment shall be conducted per section 2.2.
->After the CAPA is opened, section 7.2, 7.3 and 7.4 shall be followed for the investigation, implementation and effectiveness verification of Corrective and Preventative Action (CAPA) records respectively.
5. CAPA Process Metrics:
->The CAPA process metrics will be collected to measure the timeliness and effectiveness of the CAPA process.
->The average age of the Open CAPAs, average time taken to close the CAPAs, number of reopened CAPAs in the previous year.