The Design Control of Medical Devices includes but not limited to creation, change and reviews of design data, including but not limited to, design input document (DID), design output document (DOD), design verification records, design validation records and design history files. The Design Control of Medical Devices ensures that the changes made during the design phase are properly identified, evaluated, tested, verified, validated, approved, and documented as appropriate.The following details provides guidance to develop a process and implement a SOP for design control of medical device products to comply with ISO13485 and 21 CFR Part 820 requirements.
1.0 The Scope include: All the new medical device products or services that would be released for sale by QSI. The Design Control process begins with review and approval of the DID. The Design Change Control ends when the DMR(device master record) file is transferred to manufacturing. Any design changes made prior to release of the products will be managed through this procedure. Any process or product changes made post release will be managed through SOP0001-Document Control and Change Procedure. The level of verification and validation activities shall be appropriate for the risk of impact of the change on the quality and safety of the product. The design verification and validation shall include method/protocol, acceptance criteria and rationale for statistically valid sample size, as appropriate.
.
2.0 Define Roles and Responsibility: The Project Manager/Quality Assurance manager or the designee shall:
1.1.1 Define the design concept and the user requirements
1.1.2 Define the responsibilities and authorities involved in the design and development process.
1.1.3 Define the level of control expected in the design and development process.
1.1.4 Define the subsequent provision of products and services.
1.1.5 Determine the rigor needed for the identification, documentation, verification, validation, review, and approval of the design change being proposed.
1.1.6 Ensure that the QSI complete documentation and review of the input requirements before the development of the products are initiated.
1.1.7 Ensure that the QSI complete documentation and review of the design outputs.
1.1.8 Ensure that the design outputs results meet the design input requirements through design verification process. The design outputs are adequate for the subsequent product release process.
1.1.9 Ensure that the product design meets the user requirements through design validation process.
1.1.10 Ensure that employees are trained and their competencies verified before they are assigned any tasks or roles in the Design Control system.
1.1.11 Ensure that the documents and records from the design and development process are created, updated and maintained.
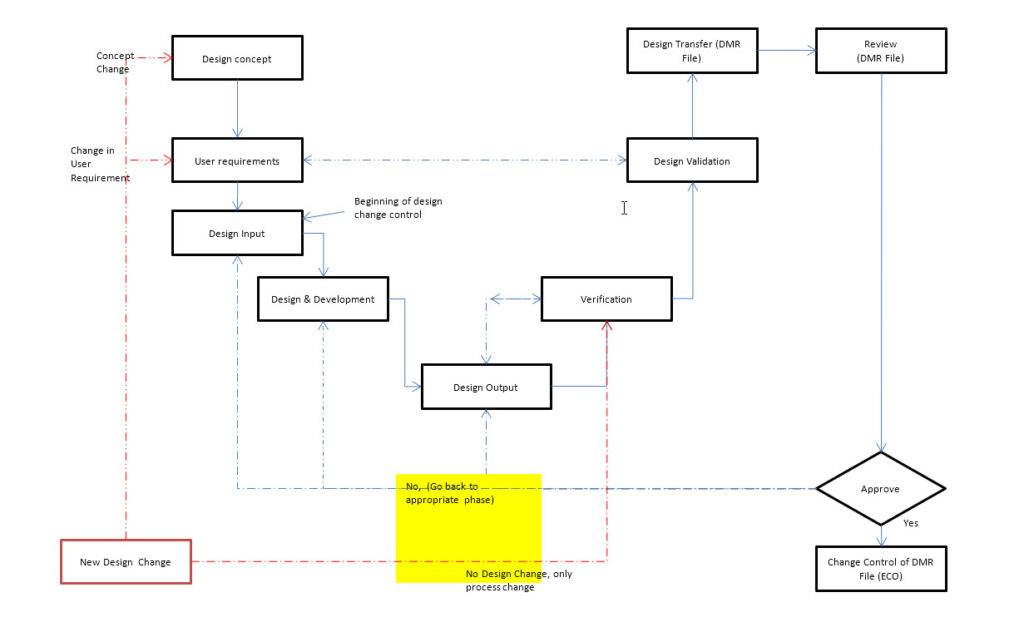
3.0 The Process/Procedure for Design Control Of Medical Devices:
1.1 When a plan is made to develop a new product, the conceptual idea shall be verified and tested using appropriate prototypes or model batches. During the review of the conceptual idea, a Risk Management file shall be created. This Risk Management file shall be updated throughout the life cycle of the product. When there is enough information available from the prototypes, the Project Manager with input from the design team shall make the decision if a new product is to be designed and developed for sale. The process for design and development shall include the stages outlined in the Figure-1. The stages in the design and development process includes following.
1.1.1 Collection of design ideas and user requirement specifications
1.1.2 Preparation of design input document (DID)
1.1.3 Review and approval of DID
1.1.4 Design and development process
1.1.5 Documentation of design output document (DOD)
1.1.6 Design Review and approval
1.1.6.1 Evaluation of the ability of the design output of the design to meet requirements.
1.1.6.2 Identify and propose necessary actions.
1.1.6.3 Participants must include representatives of functions concerned with stage being reviewed as well as other specialists.
1.1.6.4 Reviews must include representatives of all functions concerned with the design stage being reviewed and an individual who does not have direct responsibility for the design stage being reviewed (independent reviewer) and any specialists required. This must be documented using RF0098 (Design Review Attendance List).
1.1.7 Review of DOD vs, DID (design verification): Ensure that there is identification and traceability of performance and functional characteristics and the results. The purpose design verification is to ensure that the results of DOD are matching the requirements included in the DID. Any variance found shall be documented and reviewed before proceeding to next stage. The risk management document shall be updated accordingly. The design verification shall include method/protocol, acceptance criteria and rationale for statistically valid sample size, as appropriate.
1.1.8 Review of Design validation: The extent of design validation shall depend upon the performance and safety requirements for the device. The purpose of the review of design validation is to ensure that the requirements for functional and performance characteristics are matching against the user requirement specifications and regulatory requirements. The design validation shall include method/protocol, acceptance criteria and rationale for statistically valid sample size, as appropriate.
1.1.9 Any variance found shall be documented and reviewed prior to proceeding to next stage. The risk management document shall be updated accordingly.
1.1.9.1 Preparation of device master record (DMR) file: The documentations for the DMR file shall include at minimum, but not limited to
1.1.9.1.1 Description of the product, intended use/purpose, labeling and instructions for use.
1.1.9.1.2 Specifications for the product
1.1.9.1.3 Specifications or procedures for manufacturing, packaging, storage, handling and distribution
1.1.9.1.4 Procedures for monitoring and measuring including the quality control protocols.
1.1.9.1.5 Requirements for installation (if needed)
1.1.9.1.6 Requirements for servicing (if needed)
1.1.10 Review and transfer of the DMR file
1.1.10.1 The DMR file shall be reviewed by the designated approvers. If any variances found, the variance shall be documented and reviewed prior to moving to next stage.
1.1.11 Change control of the DMR file through ECO process.
1.1.11.1 Post-market changes made to the medical device product shall be controlled. The changes made to the medical device product shall be identifiable and traceable. Such changes shall be controlled through the change control process (ECR/ECO) and the Risk Management file shall be updated as appropriate.
1.1.11.2 The completed DMR file shall be controlled through the ECR (Engineering change request) process.
Internal References:
1.1 SOP0001 : Document Control and Change Procedure
1.2 RF0095 : Design Input Document
1.3 RF0096 : Design Output Document
1.4 RF0097 : Design Change Control Form
1.5 ISO13485:2016 : Medical devices- Quality management systems- Requirements for regulatory
purposes
1.6 SOP0113: SOP for QMS Risk Management
1.7 RF0135: QMS Risk Management Form
1.8 RF0098 (Design Review Attendance List).
External References:
1.1 21CFR Part 211, “Current Good Manufacturing Practices for Finished Pharmaceuticals
1.2 21 CFR Part 210, “Current Good Manufacturing Practices in Manufacturing, Processing, or Holding Drugs”
1.3 USA 21 CFR Part 801: Code of Federal Regulations, Labeling
1.4 USA 21 CFR Part 807: Code of Federal Regulations, Establishment Registration and Device Listing for Manufacturers and Initial Importers of Devices
1.5 USA 21 CFR Part 812: Code of Federal Regulations, Investigational Device Exemptions
1.6 USA 21 CFR Part 814: Code of Federal Regulations, Premarket Approval of Medical Devices
1.7 USA 21 CFR Part 820: Code of Federal Regulations, Quality System Regulations
1.8 USA 21 CFR Part 830: Code of Federal Regulations, Unique Device Identification
1.10 EN ISO 14971:2019 Medical devices – Application of risk management to medical devices
1.11 Design Control Guidance for Medical Device Manufacturers of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH), Issued March 11, 2007
1.12 FDA Guidance Document “Annual Reports for Approved Premarket Approval Applications (PMA), Guidance for Industry and Food and Drug Administration Staff”
1.13 FDA Guidance Document “30-Day Notices, 135-Day Premarket Approval (PMA) Supplements and 75-Day Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE) Supplements for Manufacturing Method or Process Changes, Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff”
1.14 Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff: Post-Market Surveillance Under Section 522 of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH), Issued April 27, 2006